9 Essential API Design Best Practices for 2025
Discover 9 actionable API design best practices for building scalable, secure, and developer-friendly APIs. Elevate your strategy with our expert guide.
In today's interconnected software ecosystem, APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) are the essential connective tissue. They are the contracts that dictate how different software components interact, making them a critical component of modern application development. The distinction between a functional API and an exceptional one, however, is found entirely in its design. A poorly designed API can create developer friction, introduce security risks, and become a significant bottleneck to scaling. Conversely, a well-designed API is a pleasure to use, secure by default, and built for future growth.
This guide moves beyond theory to provide a definitive list of actionable API design best practices. We will explore nine core principles that transform good APIs into great ones, covering everything from RESTful conventions and naming consistency to robust security and performance optimization. For developers looking to build reliable, scalable, and intuitive interfaces, mastering these practices is non-negotiable. Whether you're building a new service or refining an existing one, these guidelines will help you create a blueprint for flawless digital communication. The actionable insights here are designed to be immediately applicable, and for teams looking to accelerate this process, an integrated platform like Zemith can provide the tooling to enforce these standards from day one.
1. Use RESTful API Design Principles
One of the most foundational api design best practices is adhering to REST (Representational State Transfer) principles. REST is not a protocol but an architectural style that leverages standard HTTP methods to create predictable, scalable, and stateless APIs. It treats server-side data as a collection of resources, which can be created, retrieved, updated, or deleted using standard HTTP verbs.
This approach simplifies client-server communication by using the web's existing infrastructure. For example, a GET request retrieves data, a POST request creates new data, a PUT request updates existing data, and a DELETE request removes it. This predictable structure, seen in widely used APIs like the GitHub REST API and the Stripe API, makes development faster and more intuitive for consumers.
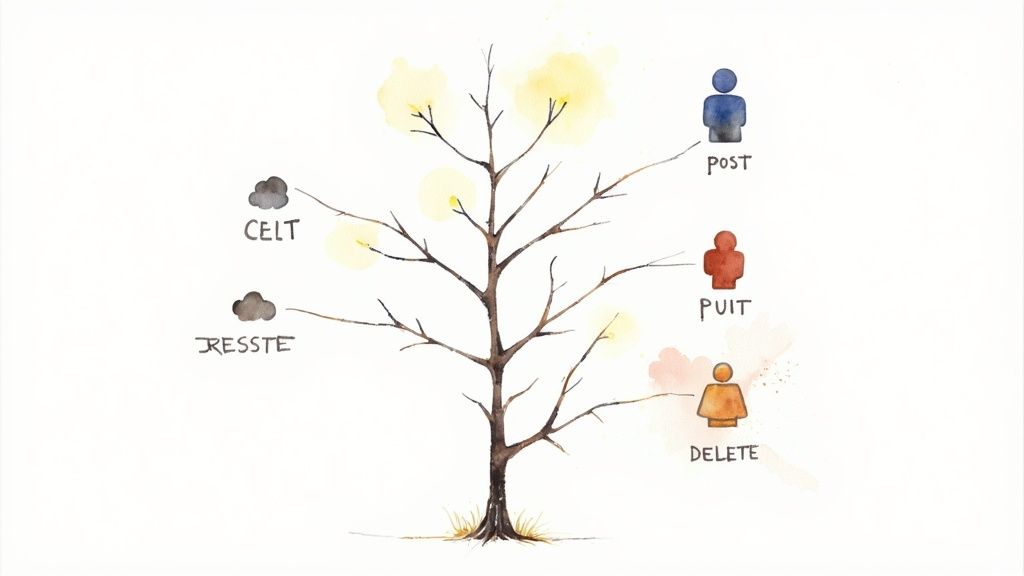
Actionable Implementation Tips
To effectively implement RESTful principles, focus on resource-oriented design and consistent communication standards. By making your API predictable, you significantly lower the learning curve for developers integrating with it.
- Use Nouns for Resources: URIs should represent resources, not actions. Use plural nouns for collections.
- Good:
GET /api/v1/users - Bad:
GET /api/v1/getAllUsers
- Good:
- Leverage HTTP Verbs: Use the appropriate HTTP method for the intended action on the resource.
GET /users/{id}: Retrieve a specific user.POST /users: Create a new user.PUT /users/{id}: Update a user's details.DELETE /users/{id}: Delete a user.
- Implement Proper Status Codes: Use standard HTTP status codes to communicate the outcome of a request. For instance,
200 OKfor success,201 Createdfor successful resource creation,400 Bad Requestfor client errors, and500 Internal Server Errorfor server issues.
Adopting REST principles ensures your API is logical and easy to use, forming a solid foundation for more advanced features. For teams looking to streamline and document their design process, platforms like Zemith offer tools that can help maintain consistency and clarity across all API endpoints.
2. Implement Consistent and Intuitive Naming Conventions
Another critical api design best practice is to establish and enforce consistent, intuitive naming conventions. Predictability is a cornerstone of a great developer experience. When API endpoints, parameters, and response fields follow a clear pattern, developers can anticipate how to interact with different parts of your API without constantly referencing documentation, which accelerates integration and reduces errors.
This practice goes beyond just choosing a casing style; it involves creating a logical and descriptive vocabulary for your API's resources and their attributes. Major platforms like the Salesforce API, which uses camelCase consistently, and the Slack API, with its intuitive method names like chat.postMessage, demonstrate how effective a strong naming strategy can be. This consistency builds trust and makes the API feel professionally crafted and reliable.

Actionable Implementation Tips
To implement effective naming conventions, your goal is to eliminate ambiguity and cognitive load for developers. A well-defined strategy, documented and enforced early, pays significant dividends as your API ecosystem grows.
- Choose One Case Convention: Decide on a casing style for all resource names, parameters, and JSON fields and stick to it. Common choices include
camelCase(e.g.,userId) orsnake_case(e.g.,user_id).- Good:
{"firstName": "Jane", "lastName": "Doe"} - Bad:
{"FirstName": "Jane", "last_name": "Doe"}
- Good:
- Use Descriptive, Unambiguous Names: Names should clearly indicate their purpose. Avoid cryptic abbreviations or acronyms that may not be universally understood.
- Good:
GET /users/{userId}/shippingAddress - Bad:
GET /usr/{id}/shipAddr
- Good:
- Create and Document Guidelines Early: Define your naming rules in a style guide. This ensures that all team members, present and future, build endpoints that follow the same pattern.
Maintaining these standards manually can be challenging. An actionable insight here is to use a collaborative API design platform like Zemith which helps teams create, share, and enforce these conventions from the start, ensuring every part of your API is consistent and intuitive.
3. Provide Comprehensive Documentation and Examples
An exceptional API can fail without clear guidance, making comprehensive documentation a crucial api design best practice. Think of your documentation as the user manual for your API; it's the primary tool developers will use to understand its capabilities and integrate it successfully. Strong documentation reduces friction, minimizes support requests, and accelerates developer onboarding.
This practice goes beyond a simple endpoint list. It involves creating a rich, interactive experience that empowers developers. Leading developer-first companies like Stripe and Twilio have set the standard with interactive documentation that includes live examples, comprehensive guides, and ready-to-use code samples, demonstrating that great documentation is a product feature in itself.
Actionable Implementation Tips
To create documentation that developers love, focus on clarity, interactivity, and completeness. The goal is to answer a developer's questions before they even have to ask them, making the integration process as seamless as possible. To ensure your API is easily adoptable and maintainable, you should follow these 7 essential API documentation best practices to cover all critical aspects.
- Use Interactive Tools: Leverage OpenAPI/Swagger specifications to automatically generate interactive documentation. Tools like Swagger UI or Redoc allow developers to test API calls directly from their browser.
- Provide Practical Code Samples: Include copy-paste-ready code snippets for common use cases in multiple programming languages (e.g., Python, JavaScript, Java).
- Detail Authentication and Errors: Clearly explain the authentication process with examples. Document every possible error code, what it means, and how developers can resolve it.
- Keep Documentation in Sync: Use automated tools and a "docs-as-code" approach to ensure your documentation always reflects the latest version of your API, preventing confusion and bugs.
Investing in high-quality documentation is a direct investment in your developer experience. For a deeper dive, explore these best practices for API documentation to elevate your developer support.
4. Implement Proper Error Handling with Meaningful Messages
A crucial aspect of developer-friendly api design best practices is implementing robust error handling with clear, actionable messages. When an API call fails, the response should empower developers to quickly diagnose and fix the problem, rather than leaving them guessing. Proper error handling involves using standard HTTP status codes combined with a detailed, consistent JSON payload that explains what went wrong.
This approach transforms a frustrating failure into a constructive debugging experience. For instance, APIs like Stripe and GitHub are renowned for their excellent error responses, which often include unique error codes, human-readable descriptions, and sometimes even links to relevant documentation. This level of detail significantly reduces integration friction and support overhead.

Actionable Implementation Tips
To build a reliable error handling system, focus on providing context and consistency in every error response. This ensures your API is predictable even when things go wrong, making it a more dependable tool for developers.
- Use Standard HTTP Status Codes: Align with web standards to signal the nature of the error.
- 4xx Codes: Use for client-side errors (e.g.,
400 Bad Requestfor invalid syntax,404 Not Foundfor a missing resource). - 5xx Codes: Reserve for server-side failures (e.g.,
500 Internal Server Error,503 Service Unavailable).
- 4xx Codes: Use for client-side errors (e.g.,
- Provide a Detailed Error Payload: Go beyond just the status code. Include a JSON object with helpful fields.
error_code: A unique identifier for programmatic handling (e.g.,invalid_api_key).message: A clear, human-readable explanation of the error.details: An object or array for field-specific validation errors (e.g.,{"field": "email", "issue": "must be a valid email address"}).request_id: A unique ID for the request, essential for logging and support.
- Document All Possible Errors: Your API documentation should clearly list potential error responses for each endpoint, explaining what they mean and how to resolve them.
Thorough error handling is not just a feature; it is a core part of the developer experience. Integrating this with a comprehensive testing strategy is key. You can find more information on this by exploring software testing best practices.
5. Design for Security with Authentication and Authorization
A critical component of any modern API is robust security, making this one of the most important api design best practices to implement. Security in this context is twofold: authentication confirms who a user is, while authorization determines what an authenticated user is permitted to do. Neglecting these aspects can expose sensitive data and leave your systems vulnerable to attacks.
Implementing industry-standard security protocols ensures that only legitimate users and applications can access your API. For example, Google APIs use OAuth 2.0 to grant secure, delegated access, while AWS Identity and Access Management (IAM) provides fine-grained control over which resources users can access. These mechanisms are fundamental for building trust and ensuring data integrity.
Actionable Implementation Tips
To build a secure API, you must integrate security from the very beginning of the design process, not as an afterthought. A layered approach ensures that if one control fails, others are in place to prevent a breach.
- Always Use HTTPS: Encrypt all data in transit by enforcing TLS/SSL across all API endpoints. This prevents man-in-the-middle attacks and protects sensitive information like credentials and tokens.
- Implement Strong Authentication: Use a standard like OAuth 2.0 for third-party access or JSON Web Tokens (JWT) for stateless authentication. Ensure tokens have a short expiration time and a clear refresh mechanism.
- Apply the Principle of Least Privilege: Grant users and applications only the permissions they absolutely need to perform their tasks. Avoid giving broad, unnecessary access to resources.
- Conduct Regular Security Audits: Proactively identify vulnerabilities by performing security checks. To ensure your API is robust against attacks, it's crucial to consider insights from penetration testing best practices.
By prioritizing security, you protect your users and your infrastructure. An actionable approach is to use tools like Zemith that can help teams document and enforce security policies consistently across all API endpoints, ensuring these critical standards are met from development to deployment.
6. Implement API Versioning Strategy
A crucial element of sustainable api design best practices is implementing a clear versioning strategy. As your API evolves, you will inevitably introduce new features, change data structures, or deprecate endpoints. Versioning allows you to manage these changes gracefully, ensuring that existing client applications continue to function without breaking while you roll out updates.
This forward-thinking approach prevents the chaos of forcing all consumers to update simultaneously. Instead, it provides a stable and predictable path for evolution. For instance, the transition from Twitter's API v1.1 to v2 and GitHub's parallel support for REST (v3) and GraphQL (v4) APIs both demonstrate how versioning can introduce significant improvements without disrupting the entire ecosystem. It signals reliability and a commitment to developer experience.
Actionable Implementation Tips
To effectively implement API versioning, you must choose a method early in the design process and apply it consistently. This predictability is key to maintaining trust with developers who rely on your API for their applications.
- Choose a Versioning Method: Decide how the version will be specified in requests. Common methods include URI path versioning, query parameters, or custom request headers.
- Good (URI):
GET /api/v2/products - Good (Header):
Accept: application/vnd.myapi.v2+json
- Good (URI):
- Use Semantic Versioning: Adopt semantic versioning (e.g., v1, v2, v3.1) to clearly communicate the nature of changes. A major version change (v1 to v2) indicates breaking changes, while minor or patch versions signal backward-compatible additions or fixes.
- Communicate Changes Clearly: Maintain a detailed changelog and provide clear migration guides when releasing new versions. Announce deprecation timelines well in advance, giving developers ample time to adapt their code to the newer version.
By planning for change from the start, you build a resilient and developer-friendly API. For a deeper look into managing these changes systematically, you can explore more on version control best practices.
7. Optimize Performance with Caching and Pagination
A crucial aspect of modern api design best practices is ensuring your API is fast, responsive, and can handle large volumes of data efficiently. Performance optimization through caching and pagination prevents server overload and provides a superior user experience by delivering data quickly and in manageable pieces.
Caching stores frequently requested data temporarily, reducing database load and latency for subsequent requests. Pagination breaks down large datasets into smaller, digestible chunks, preventing performance bottlenecks when clients request extensive collections of resources. High-traffic platforms like the GitHub API and Reddit API rely heavily on these techniques to maintain performance and scalability, ensuring their services remain responsive even under heavy load.
Actionable Implementation Tips
To effectively boost API performance, combine server-side logic with standardized HTTP mechanisms. A well-implemented caching and pagination strategy makes your API more robust, scalable, and cost-effective to operate.
- Implement HTTP Caching Headers: Use headers like
Cache-Control,ETag, andLast-Modifiedto allow clients and intermediaries (like CDNs) to cache responses. This significantly reduces unnecessary server requests. - Use Cursor-Based Pagination: For large, dynamic datasets, cursor-based pagination is often superior to offset-based methods as it avoids performance degradation on deep pages.
- Good:
GET /api/v1/items?limit=20&after_cursor=eXAmcGxl - Bad:
GET /api/v1/items?page=100&limit=20
- Good:
- Provide Configurable Page Sizes: Allow clients to specify the number of items per page via a parameter (e.g.,
limitorsize), but enforce a reasonable maximum to prevent abuse. Include metadata liketotal_countand links to thenextandpreviouspages in your response.
Optimizing performance is an ongoing process. For an actionable insight, consider using API lifecycle management tools, such as those offered by Zemith, to help enforce these performance-oriented standards consistently across all endpoints, ensuring a fast and reliable experience for all consumers.
8. Use Standard HTTP Status Codes and Methods
A core component of effective api design best practices is the correct use of standard HTTP methods and status codes. This practice leverages the web's existing communication protocol to provide clear, predictable feedback to API consumers. By using the right HTTP verb for an operation and a corresponding status code for its outcome, you create a self-describing API that developers can understand intuitively.
This standardized communication reduces ambiguity and minimizes the need for custom error-handling logic on the client side. For example, the Stripe API consistently uses 200 OK for successful requests, 400 Bad Request for client-side validation errors, and various 5xx codes for server issues. Similarly, the GitHub API correctly returns a 201 Created status when a new resource is successfully made, providing immediate, clear feedback.
Actionable Implementation Tips
To implement this best practice effectively, you must map your API's actions and outcomes to the standardized HTTP specification. Consistent and accurate use of these codes and methods is key to building a reliable and developer-friendly API.
- Use Verbs for Actions: Align HTTP methods with CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations.
GET: Retrieve resources.POST: Create new resources.PUT/PATCH: Update existing resources.DELETE: Remove resources.
- Return Accurate Status Codes: Use appropriate codes to reflect the request outcome.
201 Created: For successful resource creation, often with aLocationheader pointing to the new resource.204 No Content: For successful requests that do not return a body, like aDELETEoperation.404 Not Found: When a requested resource does not exist.429 Too Many Requests: To indicate that rate limiting has been exceeded.
- Differentiate Client and Server Errors: Clearly distinguish between errors caused by the client (
4xxcodes) and those originating on the server (5xxcodes).
Properly using HTTP standards makes your API behave predictably, fulfilling developer expectations and reducing integration friction. For teams aiming to enforce these standards across their projects, an actionable step is to adopt tools within platforms like Zemith that can help define and validate API contracts, ensuring every endpoint returns the correct status code.
9. Design APIs to be Stateless and Scalable
A critical aspect of modern api design best practices is ensuring your API is stateless. In a stateless architecture, each request from a client to the server must contain all the information needed to understand and process the request. The server does not store any session state about the client between requests, making each interaction independent and self-contained.
This approach is fundamental to building scalable and reliable systems. Because no server instance holds session-specific data, any server can handle any client request. This allows for effortless horizontal scaling, as new server instances can be added to a load balancer without complexity. APIs from major cloud providers like AWS and messaging platforms like Twilio are prime examples of stateless design, enabling them to handle massive, unpredictable workloads efficiently.
Actionable Implementation Tips
To build a truly stateless and scalable API, you must shift away from traditional session-based logic. The goal is to make each endpoint independently processable, which enhances resilience and simplifies the overall architecture.
- Include All Context in Each Request: Ensure that every request carries all necessary data, such as authentication tokens and user identifiers, so the server doesn't need to look up session information.
- Use Tokens Instead of Sessions: Implement token-based authentication (e.g., JWT, OAuth 2.0) rather than server-side sessions. The token itself contains the required user context.
- Design for Idempotency: Especially for state-changing operations, ensure that making the same request multiple times has the same effect as making it once. This prevents accidental duplication if a client retries a request.
- Decouple Services: In a microservices architecture, statelessness is key. Each service should operate independently without relying on shared session memory, facilitating isolated scaling and deployment.
By designing stateless APIs, you create a foundation that is inherently more robust and scalable. For an actionable way to implement this, teams can use platforms like Zemith to establish a structured environment for designing and documenting APIs that adhere to these core principles from the outset.
API Design Best Practices Comparison Guide
| Aspect | Use RESTful API Design Principles | Implement Consistent and Intuitive Naming Conventions | Provide Comprehensive Documentation and Examples | Implement Proper Error Handling with Meaningful Messages | Design for Security with Authentication and Authorization | Implement API Versioning Strategy | Optimize Performance with Caching and Pagination | Use Standard HTTP Status Codes and Methods | Design APIs to be Stateless and Scalable |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Implementation Complexity 🔄 | Moderate - requires understanding REST principles and HTTP | Low to moderate - requires team discipline and guidelines | High - needs dedicated effort for detailed docs and examples | Moderate - needs careful consistent error design | High - security protocols and continuous updates required | Moderate - planning and maintaining versions | Moderate to high - caching and pagination logic involved | Low - align with HTTP standards but requires discipline | Moderate - design for statelessness adds complexity |
| Resource Requirements ⚡ | Moderate - standard HTTP infrastructure usable | Low - mainly process and tooling | High - time and tools to create/maintain docs | Moderate - tooling for error handling frameworks needed | High - security infrastructure and monitoring | Moderate - documentation and version maintenance | Moderate - server and client-side handling required | Low - uses existing HTTP features | Moderate - token management and stateless design needed |
| Expected Outcomes 📊 | Scalable, predictable APIs with standard interfaces | Improved developer experience and reduced errors | Faster onboarding, higher adoption, less support burden | Faster debugging, fewer support requests, reliability | Secure API access and regulatory compliance | Smooth evolution with backward compatibility | Faster responses, lower load, better scalability | Predictable behavior, improved debugging, caching support | Highly scalable, fault tolerant, and simple deployments |
| Ideal Use Cases 💡 | RESTful resource-based APIs with CRUD operations | Teams needing consistent and maintainable API design | APIs targeting diverse developers needing guidance | APIs where error clarity speeds integration | APIs requiring robust access control and data protection | APIs expecting frequent updates and backward compatibility | High-traffic APIs handling large datasets | APIs requiring clear communication of request outcomes | Cloud-native, microservices, large-scale distributed APIs |
| Key Advantages ⭐ | Wide adoption, platform agnostic, cache-friendly | Clear, predictable API surface, easier maintenance | Developer-friendly, reduced support, increased success | Actionable errors, consistent format, improved reliability | Strong security posture, user trust, compliance | Safe enhancements without breaking clients | Enhanced speed, resource savings, scalability | Leverages HTTP standards, eases debugging | Easier scaling, simplified server design, reliability |
Streamline Your API Workflow with an AI Powerhouse
Throughout this guide, we've explored the foundational pillars of exceptional API development. From embracing RESTful principles and consistent naming conventions to implementing robust security and performance optimizations, each practice contributes to creating APIs that are not just functional, but also intuitive, scalable, and a pleasure for developers to use. Mastering these api design best practices is the difference between a brittle, confusing interface and a resilient, powerful one that serves as a solid foundation for innovation.
The core takeaway is that great API design is a holistic discipline. It's not about applying a single rule but about weaving together multiple principles into a cohesive strategy. An API with excellent documentation but poor error handling is still a flawed API. Likewise, a highly performant but insecure endpoint represents a significant liability. True mastery lies in understanding how these elements-security, scalability, usability, and maintainability-interact to create a seamless developer experience.
From Blueprint to Reality: Your Actionable Next Steps
The journey from understanding these concepts to implementing them requires both discipline and the right tools. Your immediate next steps should be to audit your current APIs against the principles we've discussed.
- Review Your Endpoints: Are your naming conventions consistent? Do you use standard HTTP methods and status codes correctly? A quick review can reveal low-hanging fruit for improvement.
- Evaluate Your Documentation: Is it comprehensive, up-to-date, and rich with examples? If not, prioritize improving it. Good documentation is one of the highest-impact investments you can make.
- Assess Your Security and Performance: Are you using modern authentication methods? Have you implemented pagination and caching where appropriate? These are critical for building trust and ensuring a reliable user experience.
Implementing these api design best practices demands meticulous attention to detail and a significant investment of time. While these principles provide the blueprint, accelerating the development process is key to staying competitive. This is where an integrated AI platform can revolutionize your workflow. Imagine using a Coding Assistant to instantly generate boilerplate code for new endpoints, debug complex authentication logic, or even draft API documentation based on your code structure.
An AI-powered suite of tools consolidates your entire development lifecycle into a single, intelligent workspace. By automating routine tasks and providing deep, contextual insights, it empowers you to focus on what truly matters: designing and building exceptional, high-performance APIs that drive your business forward.
Ready to elevate your development process and apply these api design best practices with unprecedented speed and precision? Discover how Zemith’s AI-powered workspace can help you generate cleaner code, automate documentation, and streamline your entire API lifecycle. Visit Zemith to see how you can build better APIs, faster.
Explore Zemith Features
Introducing Zemith
The best tools in one place, so you can quickly leverage the best tools for your needs.
All in One AI Platform
Go beyond AI Chat, with Search, Notes, Image Generation, and more.
Cost Savings
Access latest AI models and tools at a fraction of the cost.
Get Sh*t Done
Speed up your work with productivity, work and creative assistants.
Constant Updates
Receive constant updates with new features and improvements to enhance your experience.
Features
Selection of Leading AI Models
Access multiple advanced AI models in one place - featuring Gemini-2.5 Pro, Claude 4.5 Sonnet, GPT 5, and more to tackle any tasks

Speed run your documents
Upload documents to your Zemith library and transform them with AI-powered chat, podcast generation, summaries, and more
Transform Your Writing Process
Elevate your notes and documents with AI-powered assistance that helps you write faster, better, and with less effort
Unleash Your Visual Creativity
Transform ideas into stunning visuals with powerful AI image generation and editing tools that bring your creative vision to life

Accelerate Your Development Workflow
Boost productivity with an AI coding companion that helps you write, debug, and optimize code across multiple programming languages
Powerful Tools for Everyday Excellence
Streamline your workflow with our collection of specialized AI tools designed to solve common challenges and boost your productivity

Live Mode for Real Time Conversations
Speak naturally, share your screen and chat in realtime with AI

AI in your pocket
Experience the full power of Zemith AI platform wherever you go. Chat with AI, generate content, and boost your productivity from your mobile device.
Deeply Integrated with Top AI Models
Beyond basic AI chat - deeply integrated tools and productivity-focused OS for maximum efficiency
Straightforward, affordable pricing
Save hours of work and research
Affordable plan for power users
Plus
- 10000 Credits Monthly
- Access to plus features
- Access to Plus Models
- Access to tools such as web search, canvas usage, deep research tool
- Access to Creative Features
- Access to Documents Library Features
- Upload up to 50 sources per library folder
- Access to Custom System Prompt
- Access to FocusOS up to 15 tabs
- Unlimited model usage for Gemini 2.5 Flash Lite
- Set Default Model
- Access to Max Mode
- Access to Document to Podcast
- Access to Document to Quiz Generator
- Access to on demand credits
- Access to latest features
Professional
- Everything in Plus, and:
- 21000 Credits Monthly
- Access to Pro Models
- Access to Pro Features
- Access to Video Generation
- Unlimited model usage for GPT 5 Mini
- Access to code interpreter agent
- Access to auto tools
- 10000 Credits Monthly
- Access to plus features
- Access to Plus Models
- Access to tools such as web search, canvas usage, deep research tool
- Access to Creative Features
- Access to Documents Library Features
- Upload up to 50 sources per library folder
- Access to Custom System Prompt
- Access to FocusOS up to 15 tabs
- Unlimited model usage for Gemini 2.5 Flash Lite
- Set Default Model
- Access to Max Mode
- Access to Document to Podcast
- Access to Document to Quiz Generator
- Access to on demand credits
- Access to latest features
- Everything in Plus, and:
- 21000 Credits Monthly
- Access to Pro Models
- Access to Pro Features
- Access to Video Generation
- Unlimited model usage for GPT 5 Mini
- Access to code interpreter agent
- Access to auto tools
What Our Users Say
Great Tool after 2 months usage
simplyzubair
I love the way multiple tools they integrated in one platform. So far it is going in right dorection adding more tools.
Best in Kind!
barefootmedicine
This is another game-change. have used software that kind of offers similar features, but the quality of the data I'm getting back and the sheer speed of the responses is outstanding. I use this app ...
simply awesome
MarianZ
I just tried it - didnt wanna stay with it, because there is so much like that out there. But it convinced me, because: - the discord-channel is very response and fast - the number of models are quite...
A Surprisingly Comprehensive and Engaging Experience
bruno.battocletti
Zemith is not just another app; it's a surprisingly comprehensive platform that feels like a toolbox filled with unexpected delights. From the moment you launch it, you're greeted with a clean and int...
Great for Document Analysis
yerch82
Just works. Simple to use and great for working with documents and make summaries. Money well spend in my opinion.
Great AI site with lots of features and accessible llm's
sumore
what I find most useful in this site is the organization of the features. it's better that all the other site I have so far and even better than chatgpt themselves.
Excellent Tool
AlphaLeaf
Zemith claims to be an all-in-one platform, and after using it, I can confirm that it lives up to that claim. It not only has all the necessary functions, but the UI is also well-designed and very eas...
A well-rounded platform with solid LLMs, extra functionality
SlothMachine
Hey team Zemith! First off: I don't often write these reviews. I should do better, especially with tools that really put their heart and soul into their platform.
This is the best tool I've ever used. Updates are made almost daily, and the feedback process is very fast.
reu0691
This is the best AI tool I've used so far. Updates are made almost daily, and the feedback process is incredibly fast. Just looking at the changelogs, you can see how consistently the developers have ...
